Generators are a reliable and effective solution for ensuring uninterrupted power supply during critical situations, whether in industrial or domestic environments. They also serve as a continuous power source in specific settings, particularly in areas where access to the electrical grid is challenging or incomplete, or in situations requiring power for a limited period, such as construction sites or quarries.
Among the most popular options are diesel and gasoline generators. Each category has specific characteristics and is suited to different applications. In this article, we will explore the differences between diesel and gasoline generators. As specialists in bespoke energy solutions, Dagartech will help you determine the best option for your project.
What is a generator, and what is it used for?
A generator is a machine designed to produce electricity by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. This process is enabled by an internal combustion engine that uses fuels such as diesel or gasoline. The engine drives a generator (alternator), which converts the mechanical energy produced by combustion into electricity.
Generators can serve as a backup energy source, functioning as an emergency generator that activates during power outages and stops once the grid supply is restored. They can also act as the primary power source in off-grid areas or provide temporary support for professionals working in locations without electrical connections.
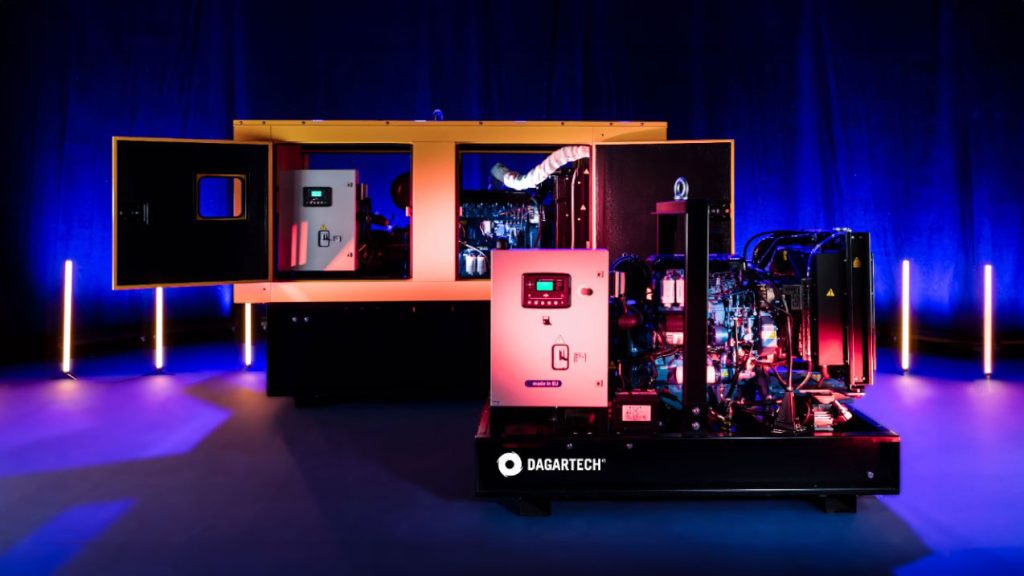
Characteristics of Diesel Generators
Efficiency and fuel consumption
Diesel is more efficient in terms of consumption compared to gasoline. Diesel generators tend to have lower operating costs in the medium and long term for this reason. However, power requirements will always be the key factor limiting decision-making, as this variable is closely tied to consumption.
Durability and maintenance
Diesel engines are designed to handle heavier and more variable loads over extended periods, making them the best choice for industrial applications requiring medium to high power. Although they require regular maintenance, their maintenance intervals are longer than those of gasoline generators, and their lifespan is significantly greater.
Characteristics of Gasoline Generators
Cost and availability
Within the same power range, gasoline generators are typically more affordable than diesel generators. They are ideal for small-scale tasks and intermittent applications.
Ease of start and maintenance
Thanks to the volatility of gasoline, these generators offer quicker starts and a more responsive energy supply. However, they require more frequent maintenance due to the nature of the fuel and the wear and tear on engine components.
Key differences between diesel and gasoline generators
Fuel consumption and operating costs
Over time, diesel generators are more efficient and cost-effective due to their lower fuel consumption. However, gasoline generators are more economical upfront and suitable for low-energy-demand projects.
Lifespan and durability
Diesel generators have a significantly longer lifespan, especially those operating at 1500 rpm. This makes them a more suitable choice for industrial applications or long-term projects. Gasoline generators, operating at 3000 rpm, represent an older and less durable technology. While lighter and easier to transport, they are intended for sporadic and temporary use.
Specific applications
Diesel generators are ideal for medium to high-power needs, whether for continuous operation or emergency use, while gasoline generators are better suited to small-scale construction tasks or low-power, portable applications.
Applications of diesel and gasoline generators
Applications of Diesel Generators:
- Industrial use in factories, production plants, or similar settings. Units such as the DGVS 770 ST or the DGPS 1250 ME are already part of major industries.
- Emergency power supply in data centres, where stability and energy efficiency are critical.
- Construction and mining projects, requiring continuous energy under demanding conditions and medium to high power output. In this context, rental generators are often the most convenient choice.
Applications of Gasoline Generators:
- Small-scale construction tasks or supporting professionals using power tools. The DGB 24 TF BC model is the most powerful in the range, exceeding 24 kVA of power.
- Residential use as a temporary backup during power outages.
- Solar support, ensuring grid failure functionality or providing stability for such applications.
- Outdoor events requiring lightweight, compact generators. Inverter models, for example, are ideal for these scenarios.
- Short-term projects or those with low energy demands.
Conclusion: Which generator is right for you?
The decision between a diesel or gasoline generator depends on the specific needs of your project or application, with power being one of the most critical factors influencing the choice.
At Dagartech, we provide expert advice to help you select the smartest solution for each case. If you have questions about which type of generator is most suitable for your needs, do not hesitate to contact us.